Briefly Describe Atp and How It Is Involved in Metabolism.
Metabolism -- Metabolism is defined as the sum of all chemical reactions required to support cellular functions in the body. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed.

Overview Of Metabolic Reactions Anatomy And Physiology Ii
The second stage of glucose catabolism comprises reactions 6 through 10 in which a net gain of ATP is achieved through the oxidation of one of the triose phosphate compounds formed in step 5.

. Muscle contractions are fueled by adenosine triphosphate ATP an energy-storing molecule. The metabolism of aspirin in the small intestine accelerates to distribute it to organs and tissues throughout the body. Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level.
ATP serves as a bearer of chemical energy in metabolism more specifically in cellular respiration. In catabolism metabolic pathways are organised such that energy is released slowly in discrete quanta of energy which is captured by the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate ATP guanosine triphosphate GTP NADPH nicotinamide adenine nucleotide phosphate or by the electron transport chain ETC. The ATP is formed from both the fatty acid spiral and the citric acid cycle.
Cells are constantly carrying out thousands of chemical reactions needed to keep the cell and your body as a whole alive and healthy. There are many mitochondria in animal tissuesfor example in. ATP is a compound that stores and transports energy within a cell.
Briefly describe ATP and how it is involved in metabolism. Describe how energy is. The cells then break down ATP releasing energy as they engage in a variety of activities explain Drs.
Describe how energy is involved in catabolism. ATP is a relatively small molecule that serves as an energy intermediate in human metabolism. ATP is a reservoir of potential chemical energy and acts as a common intermediate in metabolism linking energy requiring and energy yielding reactions.
Metabolism is the total amount of the biochemical reactions involved in maintaining the living condition of the cells in an organism. The formation of ATP. Glycolysis the Krebs Cycle the electron transport chain During glycolysis ATP is first used to invest energy in glucose as to allow for its subsequent breakdown into pyruvate.
Briefly describe ATP and how it is involved in metabolism. All of the chemical reactions that take place inside of a cell are collectively called the cells metabolism. Provide 3 full evidence-based APA citations.
Briefly describe atp and how it is involved in metabolism. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate consisting of a nitrogenous base adenine a ribose sugar and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is composed of one.
Briefly describe how ATP energy molecules are extracted from the chemical bond energy in glucose. Adenosine triphosphate also known as ATP is a molecule that carries energy within cells. The body is a complex organism and as such it takes energy to maintain proper functioning.
ATP synthesis in mitochondria. However the liver seems to be the primary focus for further metabolizing. Connections to Electron Transport and ATP.
Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate ATP. One turn of the fatty acid spiral produces ATP from the interaction of the coenzymes FAD step 1 and NAD step 3 with the electron transport chain. Cellular respiration metabolism comes in three steps.
Up to 80 of the metabolism of aspirin takes place in the liver where it undergoes rapid chemical changes in combination with the livers acids and. All living organisms require energy for different essential processes and for producing new organic substances. ATP is a compound that stores and transports energy within a cell.
Pyruvate i s converted to acetyl-CoA which is the starting material for the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids and by the reverse process fatty acids are converted to glucose whereas the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction is essentially nonreversible which prevents the direct. All living things use ATP. Explain what anabolism is and give a couple of good examples of anabolism in the body.
Describe how energy is involved in catabolism. Energy is transferred from molecules such as glucose to an intermediate energy source ATP. Both three-carbon fragments follow the same pathway and steps 6 through 10.
In essence your cells extract the chemical energy from various nutrient molecules like proteins carbohydrates and proteins and use the chemical energy to make ATP. Answer one or more of these. Answer one or more of these.
These chemical reactions are often linked together in chains or pathways. In order to understand the mechanism by which the energy released during respiration is conserved as ATP it is necessary to appreciate the structural features of mitochondriaThese are organelles in animal and plant cells in which oxidative phosphorylation takes place. ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest.
Total ATP per turn of the fatty acid spiral is. Metabolism Metabolism is defined as the sum of all chemical reactions required to support cellular functions in the body. One molecule of glucose forms two molecules of the triose phosphate.
The molecule containing high-energy bonds used to transfer energy between systems within a cell. ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system. It is beyond the scope of this review to address the metabolic switches occurring in compensated hypertrophy.
Four potential sources of ATP power muscle contractions. Explain what catabolism is and give a couple of good examples of catabolism in the body. ATP is an important source of energy for biological processes.
It is the main energy currency of the cell and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light cellular respiration and fermentation. Necessity for Metabolism of Protein Fat and Carbohydrate. ATP is composed of one.
Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism particularly in energy transfer within cells. It will briefly describe the energy metabolism of normal heart and skeletal muscles and their alterations in chronic heart failure.
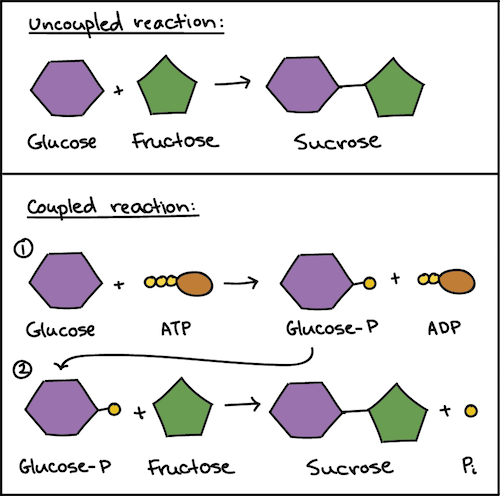
Atp Cycle And Reaction Coupling Energy Article Khan Academy
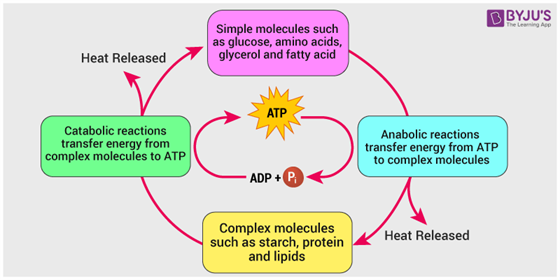

No comments for "Briefly Describe Atp and How It Is Involved in Metabolism."
Post a Comment